The evolution of smart home technology has moved steadily from novelty to infrastructure. Devices like learning thermostats, remote-controlled lighting, and intelligent energy monitors are no longer limited to early adopters. Instead, they are becoming integrated into the baseline expectation of a modern home.
Every connected device feeds into a live model of electricity demand that can be tracked, forecast, and influenced. This is precisely what large grid operators are now building toward. In India, for example, digitalisation of the national power grid is being treated as a central enabler of its energy transition. The effort is about embedding digital intelligence across the grid to handle decentralised generation, variable loads, and growing renewable inputs.
Modern substations are now being equipped with advanced control systems that allow remote management, predictive maintenance, and automatic fault detection. These upgrades reduce downtime, improve reliability, and enable far more flexible integration of solar, wind, and storage. On the edge, smart meters and sensors give operators visibility into consumption patterns at a granular level, allowing for real-time adjustments that reduce waste and defer infrastructure spending.
The intelligence being built into homes is creating new demands, and new opportunities, for the systems that deliver energy. At the same time, as grids become more adaptive, the value proposition for smart devices grows.
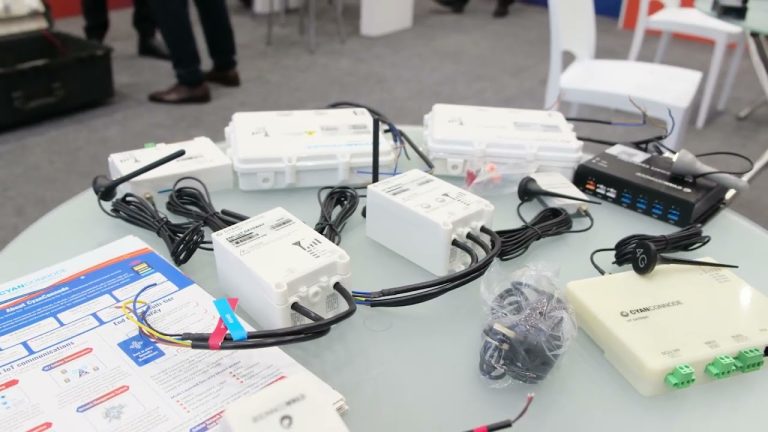
CyanConnode Holdings plc (LON:CYAN) is a world leader in the design and development of Narrowband RF mesh networks that enable Omni Internet of Things (IoT) communications.